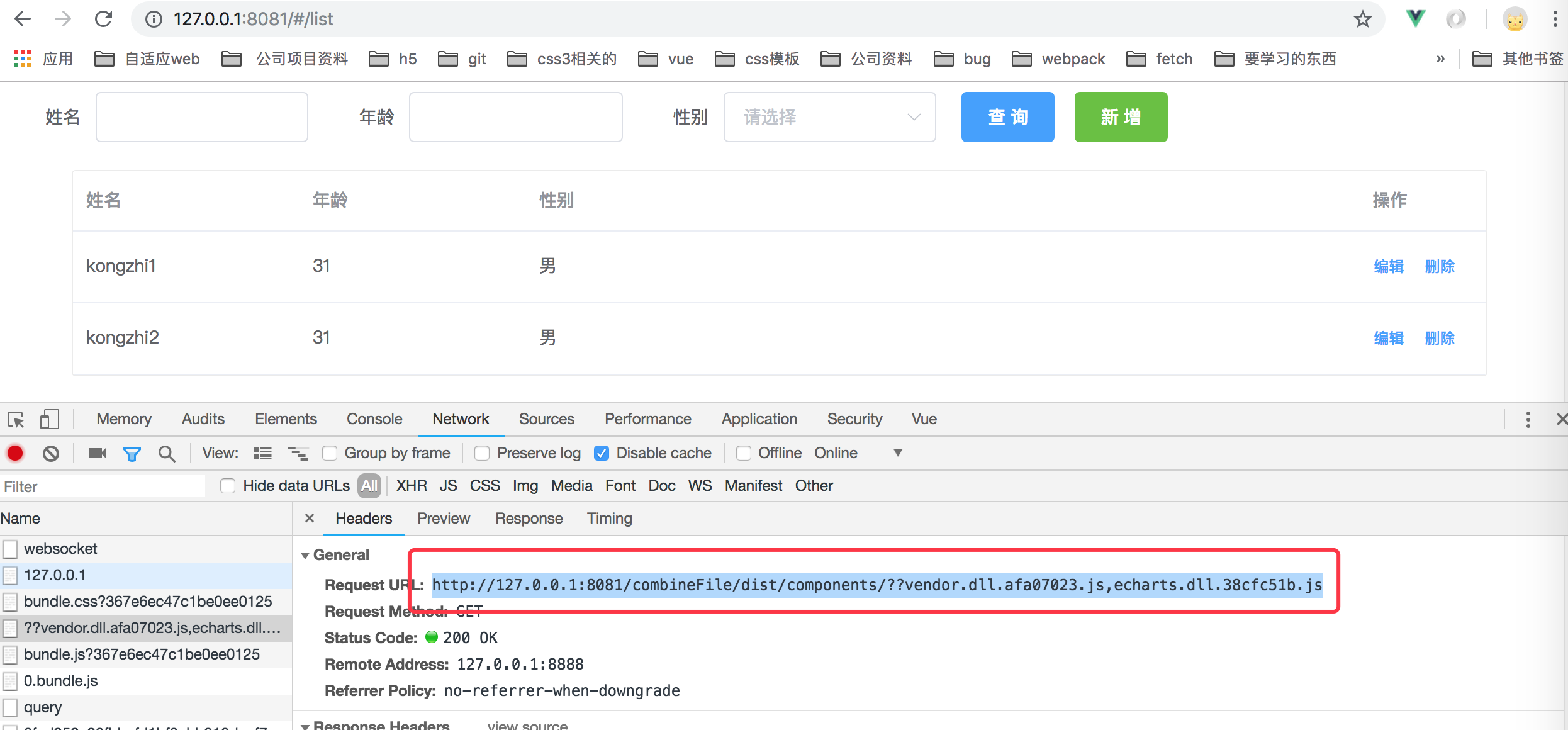
本文学习使用nodejs实现css或js资源文件的合并请求功能,我们都知道在一个复杂的项目当中,可能会使用到很多第三方插件,虽然目前使用vue开发系统或者h5页面,vue组件够用,但是有的项目中会使用到类似于echarts这样的插件,或者第三方其他的插件,比如ztree.js这样的,那如果我们把所有js都打包到一个js文件当中,那么该js可能会变得非常大,或者我们可能会把他们单独打包一个个js文件去,然后在页面中分别一个个使用script标签去引入他们,但是这样会导致页面多个js请求。因此就想使用node来实现类似于combo功能,比如以下的js功能构造:
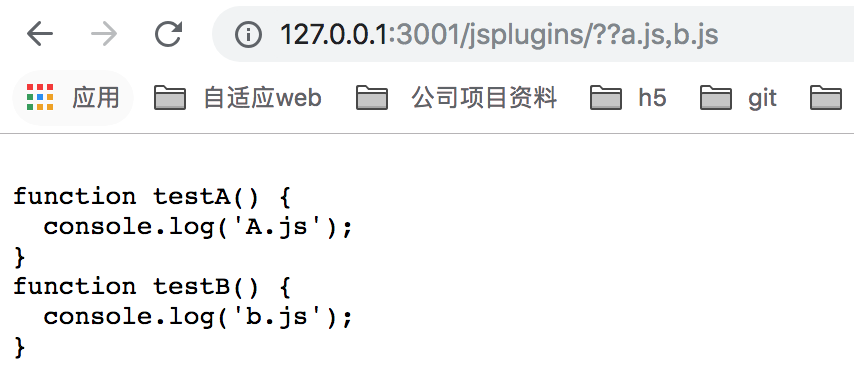
http://127.0.0.1:3001/jsplugins/??a.js,b.js
如上的js请求,会把a.js和b.js合并到一个请求里面去, 然后使用node就实现了combo功能。
首先我们来分析下上面的请求,该请求中的 ?? 是一个分隔符,分隔符前面是合并的文件路径,后面是合并资源文件名,多个文件名使用逗号(,)隔开,知道了该请求的基本原理之后,我们需要对该请求进行解析,解析完成后,分别读取该js文件内容,然后分别读取到内容后合并起来输出到浏览器中。首先看下我们项目简单的目录架构如下:
### 目录结构如下:demo1 # 工程名 | |--- node_modules # 所有的依赖包| |--- jsplugins| | |-- a.js| | |-- b.js| |--- app.js| |--- package.json
项目截图如下:
jsplugins/a.js 内容如下:
function testA() { console.log('A.js'); } jsplugins/b.js 内容如下:
function testB() { console.log('b.js');} 当我们访问 http://127.0.0.1:3001/jsplugins/??a.js,b.js 请求后,资源文件如下:
如何实现呢?
app.js 一部分代码如下:
// 引入express模块const express = require('express');const fs = require('fs');const path = require('path');// 创建app对象const app = express();app.use((req, res, next) => { const urlInfo = parseURL(__dirname, req.url); console.log(urlInfo); if (urlInfo) { // 合并文件 combineFiles(urlInfo.pathnames, (err, data) => { if (err) { res.writeHead(404); res.end(err.message); } else { res.writeHead(200, { 'Content-Type': urlInfo.mime }); res.end(data); } }); }});// 定义服务器启动端口 app.listen(3001, () => { console.log('app listening on port 3001');}); 如上代码,使用express实现一个简单的,端口号为3001的服务器,然后使用 app.use模块截取请求,比如我们现在在浏览器中访问 http://127.0.0.1:3001/jsplugins/??a.js,b.js 这个请求的时候,会对该请求进行解析,会调用 parseURL方法,该方法的代码如下:
let MIME = { '.css': 'text/css', '.js': 'application/javascript'};// 解析文件路径function parseURL(root, url) { let base, pastnames, separator; if (url.indexOf('??') > -1) { separator = url.split('??'); base = separator[0]; pathnames = separator[1].split(',').map((value) => { const filepath = path.join(root, base, value); return filepath; }); return { mime: MIME[path.extname(pathnames[0])] || 'text/plain', pathnames: pathnames } } return null;}; 如上代码,给parseURL函数传递了两个参数,一个是 __dirname 和 req.url, 其中__dirname就是当前app.js文件的所在目录,因此会打印出该目录下全路径:/Users/tugenhua/个人demo/webpack-all-demo2/webpack-all-demo/webpack+node合并js资源请求文件, req.url返回的是url中的所有信息,因此 req.url='/jsplugins/??a.js,b.js', 然后判断url中是否有 ?? 这样的,找到的话,就使用 ?? 分割,如下代码:
separator = url.split('??');
base = separator[0];因此 base = '/jsplugins/', separator[1] = a.js,b.js了,然后再进行对 separator[1] 使用逗号(,) 分割变成数组进行遍历a.js和b.js了,遍历完成后,如代码 const filepath = path.join(root, base, value); 使用path.join()对路径进行合并,该方法将多个参数值字符串结合为一个路径字符串,path.join基本使用,看我这篇文章
(),root = '/Users/tugenhua/个人demo/webpack-all-demo2/webpack-all-demo/webpack+node合并js资源请求文件'base = '/jsplugins/';value = 'a.js' 或 value = 'b.js';
因此 pathnames 的值最终变成如下的值:
[ '/Users/tugenhua/个人demo/webpack-all-demo2/webpack-all-demo/webpack+node合并js资源请求文件/jsplugins/a.js', '/Users/tugenhua/个人demo/webpack-all-demo2/webpack-all-demo/webpack+node合并js资源请求文件/jsplugins/b.js' ]
执行完parseURL后返回的是如下对象:
{ mime: 'application/javascript', pathnames: [ '/Users/tugenhua/个人demo/webpack-all-demo2/webpack-all-demo/webpack+node合并js资源请求文件/jsplugins/a.js', '/Users/tugenhua/个人demo/webpack-all-demo2/webpack-all-demo/webpack+node合并js资源请求文件/jsplugins/b.js' ] } path.extname 的使用可以看如下这篇文章(),就是拿到路径的扩展名,那么拿到的扩展名就是 .js, 然后 mime = MIME[path.extname(pathnames[0])] || 'text/plain', 因此 mine = 'application/javascript' 了。
返回值后,就会执行如下代码:
if (urlInfo) { // 合并文件 combineFiles(urlInfo.pathnames, (err, data) => { if (err) { res.writeHead(404); res.end(err.message); } else { res.writeHead(200, { 'Content-Type': urlInfo.mime }); res.end(data); } });} 先合并文件,文件合并后,再执行回调,把合并后的js输出到浏览中,先看下 combineFiles 函数的方法代码如下:
//合并文件function combineFiles(pathnames, callback) { const output = []; (function nextFunc(l, len){ if (l < len) { fs.readFile(pathnames[l], (err, data) => { if (err) { callback(err); } else { output.push(data); nextFunc(l+1, len); } }) } else { const data = Buffer.concat(output); callback(null, data); } })(0, pathnames.length);} 首先该方法传了 pathnames 和callback回调,其中pathnames的值是如下:
[ '/Users/tugenhua/个人demo/webpack-all-demo2/webpack-all-demo/webpack+node合并js资源请求文件/jsplugins/a.js', '/Users/tugenhua/个人demo/webpack-all-demo2/webpack-all-demo/webpack+node合并js资源请求文件/jsplugins/b.js' ]
然后一个使用立即函数先执行,把 0, 和 长度参数传递进去,判断是否小于文件的长度,如果是的话,就是 fs中的读取文件方法 (readFile), 就依次读取文件,对 readFile读取文件的方法不熟悉的话,可以看这篇文章(), 读取完后使用 Buffer.concat进行拼接。最后把数据传给callback返回到回调函数里面去,执行回调函数,就把对应的内容输出到浏览器中了。
注意:
1. 使用 fs.readFile 方法,如果没有设置指定的编码,它会以字节的方式读取的,因此使用Buffer可以进行拼接。2. 使用Buffer.concat拼接的时候,如果a.js或b.js有中文的话,会出现乱码,出现的原因是如果js文件是以默认的gbk保存的话,那么我们nodejs默认是utf8读取的,就会有乱码存在的,因此js文件如果是本地的话,尽量以utf8保存。如果不是utf8保存的话,出现了乱码,我们需要解决,下一篇文章就来折腾下 Buffer出现乱码的情况是如何解决的。因此整个app.js 代码如下:
// 引入express模块const express = require('express');const fs = require('fs');const path = require('path');// 创建app对象const app = express();app.use((req, res, next) => { const urlInfo = parseURL(__dirname, req.url); console.log(urlInfo); if (urlInfo) { // 合并文件 combineFiles(urlInfo.pathnames, (err, data) => { if (err) { res.writeHead(404); res.end(err.message); } else { res.writeHead(200, { 'Content-Type': urlInfo.mime }); res.end(data); } }); }});let MIME = { '.css': 'text/css', '.js': 'application/javascript'};// 解析文件路径function parseURL(root, url) { let base, pastnames, separator; if (url.indexOf('??') > -1) { separator = url.split('??'); base = separator[0]; pathnames = separator[1].split(',').map((value) => { const filepath = path.join(root, base, value); return filepath; }); return { mime: MIME[path.extname(pathnames[0])] || 'text/plain', pathnames: pathnames } } return null;};//合并文件function combineFiles(pathnames, callback) { const output = []; (function nextFunc(l, len){ if (l < len) { fs.readFile(pathnames[l], (err, data) => { if (err) { callback(err); } else { output.push(data); nextFunc(l+1, len); } }) } else { const data = Buffer.concat(output); callback(null, data); } })(0, pathnames.length);}// 定义服务器启动端口 app.listen(3001, () => { console.log('app listening on port 3001');}); 二:combo功能合并资源文件后如何在项目中能实战呢?
如上使用node实现了资源文件combo功能后,我们会把该技术使用到项目中去,那么这个项目还是我们之前的这篇文章的项目---
目录结构还是和以前一样的,如下所示:
### 目录结构如下:demo1 # 工程名| |--- dist # 打包后生成的目录文件 | |--- node_modules # 所有的依赖包| |----database # 数据库相关的文件目录| | |---db.js # mongoose类库的数据库连接操作| | |---user.js # Schema 创建模型| | |---addAndDelete.js # 增删改查操作| |--- app| | |---index| | | |-- views # 存放所有vue页面文件| | | | |-- list.vue # 列表数据| | | | |-- index.vue| | | |-- components # 存放vue公用的组件| | | |-- js # 存放js文件的| | | |-- css # 存放css文件| | | |-- store # store仓库| | | | |--- actions.js| | | | |--- mutations.js| | | | |--- state.js| | | | |--- mutations-types.js| | | | |--- index.js| | | | || | | |-- app.js # vue入口配置文件| | | |-- router.js # 路由配置文件| |--- views| | |-- index.html # html文件| |--- webpack.config.js # webpack配置文件 | |--- .gitignore | |--- README.md| |--- package.json| |--- .babelrc # babel转码文件| |--- app.js # express入口文件
唯一不同的是,在webpack.dll.config.js 对公用的模块进行打包会把 vue 和 echarts 会打包成二个文件:
module.exports = { // 入口文件 entry: { // 项目中用到该依赖库文件 vendor: ['vue/dist/vue.esm.js', 'vue', 'vuex', 'vue-router', 'vue-resource'], echarts: ['echarts'] }, // 输出文件 output: { // 文件名称 filename: '[name].dll.[chunkhash:8].js', // 将输出的文件放到dist目录下 path: path.resolve(__dirname, './dist/components'), /* 存放相关的dll文件的全局变量名称,比如对于jquery来说的话就是 _dll_jquery, 在前面加 _dll 是为了防止全局变量冲突。 */ library: '_dll_[name]' },} 因此会在我们项目中 dist/components/ 下生成两个对应的 vendor.dll.xx.js 和 echarts.dll.xx.js, 如下所示
:
然后把 刚刚的js代码全部复制到我们的 该项目下的 app.js 下:如下代码:
// 引入express模块const express = require('express');// 创建app对象const app = express();const addAndDelete = require('./database/addAndDelete');const bodyParser = require("body-parser");const fs = require('fs');const path = require('path');app.use(bodyParser.json());app.use(bodyParser.urlencoded({ extended: false }));// 使用app.use('/api', addAndDelete);let MIME = { '.css': 'text/css', '.js': 'application/javascript'};app.use((req, res, next) => { const urlInfo = parseURL(__dirname, req.url); if (urlInfo) { // 合并文件 combineFiles(urlInfo.pathnames, (err, data) => { if (err) { res.writeHead(404); res.end(err.message); } else { res.writeHead(200, { 'Content-Type': urlInfo.mime }); res.end(data); } }); }});// 解析文件路径function parseURL(root, url) { let base, pastnames, separator; if (url.indexOf('??') > -1) { separator = url.split('??'); base = separator[0]; pathnames = separator[1].split(',').map((value) => { const filepath = path.join(root, base, value); return filepath; }); return { mime: MIME[path.extname(pathnames[0])] || 'text/plain', pathnames: pathnames } } return null;};//合并文件function combineFiles(pathnames, callback) { const output = []; (function nextFunc(l, len){ if (l < len) { fs.readFile(pathnames[l], (err, data) => { if (err) { callback(err); } else { output.push(data); nextFunc(l+1, len); } }) } else { const data = Buffer.concat(output); callback(null, data); } })(0, pathnames.length);}// 定义服务器启动端口 app.listen(3001, () => { console.log('app listening on port 3001');}); 如上完成后,在我们的页面引入该合并后的js即可:index.html 如下引入方式:
如上引入,为什么我们的js前面会使用 combineFile 这个目录呢,这是为了解决跨域的问题的,因此我们app.js 是在端口号为3001服务器下的,而我们的webpack4的端口号8081,那页面直接访问 http://localhost:8081/#/list 的时候,肯定会存在跨域的情况下,因此前面加了个 combineFile文件目录,然后在我们的webpack中的devServer.proxy会代理下实现跨域,如下配置:
module.exports = { devServer: { port: 8081, // host: '0.0.0.0', headers: { 'X-foo': '112233' }, inline: true, overlay: true, stats: 'errors-only', proxy: { '/api': { target: 'http://127.0.0.1:3001', changeOrigin: true // 是否跨域 }, '/combineFile': { target: 'http://127.0.0.1:3001', changeOrigin: true, // 是否跨域, pathRewrite: { '^/combineFile' : '' // 重写路径 } } } }} 对请求为 '/combineFile' 会把它代理到 'http://127.0.0.1:3001',下,并且pathRewrite这个参数重写路径,以'^/combineFile' : '' 开头的,会替换成空,因此当我们使用肉眼看到的如下这个请求:
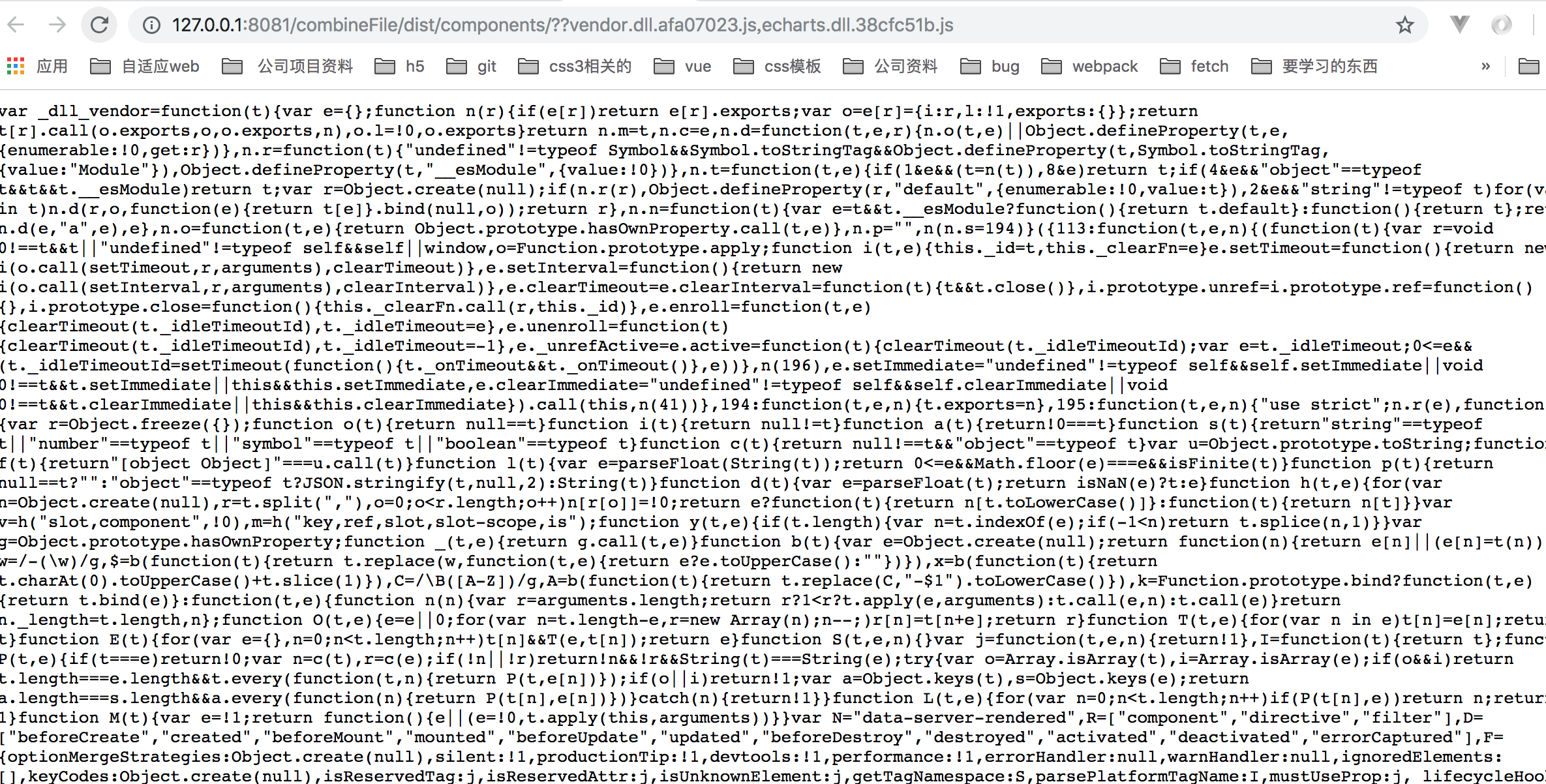
http://127.0.0.1:8081/combineFile/dist/components/??vendor.dll.afa07023.js,echarts.dll.38cfc51b.js它会被转义成 :
http://127.0.0.1:3001/dist/components/??vendor.dll.afa07023.js,echarts.dll.38cfc51b.js这个请求,因此就不会跨域了。如下所示: